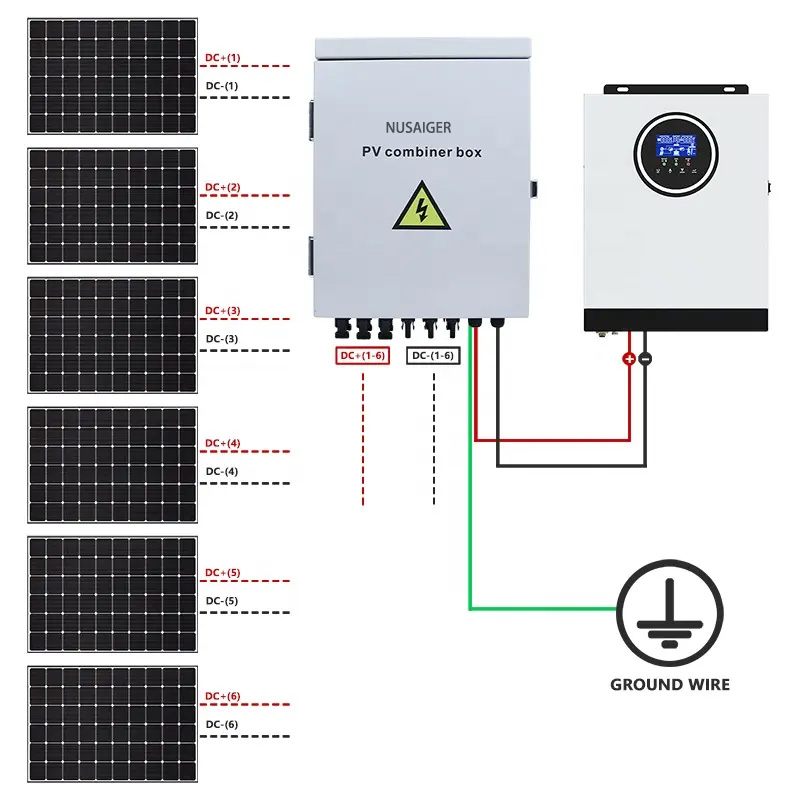
Introduction
A PV combiner box is more than just a junction point in a photovoltaic system—it’s a hub of functionality that consolidates incoming DC power, houses critical safety features, and serves as a monitoring interface in modern smart solar systems. Like any electrical component operating under harsh environmental and electrical conditions, combiner boxes are subject to wear, damage, and failure over time.
Effective troubleshooting and scheduled maintenance are crucial not only for ensuring safety but also for maintaining optimal system performance and avoiding costly downtime. This article delivers an in-depth look into practical, field-tested strategies for diagnosing problems and implementing routine maintenance procedures for PV combiner boxes.
Chapter 1: Understanding the Structure and Functionality of a PV Combiner Box
Before diving into troubleshooting, it’s vital to understand what components you’ll encounter inside a combiner box:
-
DC input terminals: Receive power from strings of PV modules.
-
Fuses or circuit breakers: Protect individual strings.
-
Busbars: Combine currents into a single output.
-
Surge Protective Devices (SPDs): Protect against transient voltage.
-
Monitoring devices (in smart boxes): Track voltage, current, temperature.
-
Output terminals: Send power to the inverter or DC disconnect.
Understanding how these components interact helps pinpoint potential failure points.
Chapter 2: Common Issues in PV Combiner Boxes
2.1 Loose or Corroded Connections
Symptoms:
-
Voltage drops
-
Heat generation
-
Arcing or burn marks
Causes:
-
Thermal cycling loosening screw terminals
-
Moisture ingress
Prevention:
-
Use torque drivers to tighten to manufacturer specs
-
Apply anti-corrosion paste
2.2 Blown Fuses or Tripped Breakers
Symptoms:
-
One or more PV strings not producing power
-
Alarm indicators or inverter warnings
Common Causes:
-
Ground faults in the string
-
Short circuits
-
Faulty PV modules
Solution:
-
Isolate affected string
-
Use insulation resistance tester (megger)
-
Replace fuses only after diagnosing root cause
2.3 Surge Protection Device (SPD) Failure
Symptoms:
-
No visible indicator on SPD
-
Combiner box stopped operating after storm
Prevention:
-
Visual inspection of SPD status LEDs
-
Use of thermal cameras to detect pre-failure heating
2.4 Water Ingress or Condensation
Symptoms:
-
Moisture droplets
-
Corrosion on terminals
-
Tripped protection devices
Root Causes:
-
Improper sealing
-
Broken gaskets
-
Open cable glands
Remedy:
-
Reseal or replace damaged gaskets
-
Use breather vents with desiccant
-
Install combiner boxes under protective covers
2.5 Rodent or Insect Infestation
Symptoms:
-
Chewed wires
-
Nests inside enclosure
Preventive Measures:
-
Use metal gland plates and fine mesh screens
-
Periodic inspection, especially in rural areas
Chapter 3: Troubleshooting Guide – Step-by-Step
Here’s a typical PV combiner box troubleshooting procedure used in the field:
| Step | Action | Tools Required |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Turn off the DC isolator | Safety gloves, eye protection |
| 2 | Open box and inspect visually | Flashlight, camera |
| 3 | Test voltage on each string | Multimeter |
| 4 | Check continuity of fuses | Continuity tester |
| 5 | Inspect SPD functionality | Visual/LED indicators |
| 6 | Measure insulation resistance | Megger |
| 7 | Scan with thermal imager | Infrared camera |
| 8 | Document issues and proceed with repairs | Inspection report form |
Always adhere to lockout-tagout (LOTO) protocols and local electrical safety standards.
Chapter 4: Scheduled Maintenance Best Practices
4.1 Frequency of Maintenance
-
Quarterly for commercial and utility systems
-
Bi-annually for residential systems
-
Immediately after extreme weather events
4.2 Recommended Maintenance Tasks
| Task | Description |
|---|---|
| Visual inspection | Check for dirt, pests, corrosion, and damage |
| Torque testing | Verify all terminals are properly tightened |
| Fuse testing | Ensure all fuses are intact and functioning |
| SPD check | Replace worn-out SPDs based on manufacturer specs |
| Thermographic imaging | Identify overheating components early |
| Enclosure sealing | Check IP rating, tighten glands, and seals |
4.3 Tools and Equipment
-
Torque screwdriver
-
Multimeter
-
Megger
-
Thermal imaging camera
-
Cleaning supplies (alcohol wipes, dry cloths)
-
Spare fuses, SPD modules, terminals
Chapter 5: Case Studies and Lessons from the Field
Case Study 1: Inverter Repeatedly Shutting Down
Root Cause: One PV string showed intermittent connectivity. A thermal scan revealed a loose busbar terminal causing intermittent arcing.
Resolution: Re-tightening the busbar terminal and applying anti-oxidation compound resolved the issue.
Case Study 2: Lightning-Induced Combiner Box Failure
Problem: Combiner box stopped outputting power after a thunderstorm.
Diagnosis: SPD indicators had tripped.
Action: Replaced SPD module. Added additional lightning rod grounding for protection.
Case Study 3: Rodent-Induced Short Circuit
Details: Found rodent nest inside combiner box chewing on DC cables.
Fix: Replaced damaged wires and installed rodent mesh and deterrent chemicals.
Chapter 6: Upgrading Old Combiner Boxes
If your PV system is over 5–8 years old, it may be time to upgrade:
| Reason for Upgrade | Newer Feature |
|---|---|
| No remote monitoring | Add real-time SCADA or IoT sensors |
| Manual fuses only | Add resettable breakers |
| Weak enclosures | Upgrade to NEMA 4X or IP65+ |
| Lack of SPD | Add Type 1 or 2 surge protection |
Upgrades can reduce long-term O&M costs significantly.
Chapter 7: Training and Safety
-
Train staff in electrical safety and LOTO
-
Use checklists for each maintenance session
-
Record all issues, repairs, and upgrades
-
Always wear PPE when servicing combiner boxes
Conclusion
The performance of your entire PV system depends heavily on the reliability of the combiner box. Ignoring maintenance or troubleshooting delays can lead to system-wide inefficiencies, safety hazards, or financial loss due to downtime.
Through scheduled inspections, proper diagnostics, use of modern tools, and a proactive approach to field issues, you can extend the lifespan and improve the performance of your PV combiner box—and your entire solar installation.
✅ Need expert help or ready-to-install combiner boxes? Contact our team for professional-grade solar components and free technical consultation.