How to Choose the Right PV Combiner Box for Your Solar Power System
Word Count Target: ~10,000 words
1. Introduction
Selecting the right PV combiner box is one of the most crucial steps in building a reliable and efficient solar photovoltaic (PV) system. While solar panels and inverters often receive the most attention, the combiner box is equally important because it acts as the “bridge” between the solar array and the inverter. Choosing an improper combiner box can lead to electrical faults, efficiency losses, or even system downtime.
This comprehensive guide will walk you through every important factor to consider when choosing a PV combiner box, from technical specifications and protective features to environmental considerations and international standards. By the end, you will have a clear roadmap to selecting the best combiner box for your unique project needs.
2. Role of the PV Combiner Box in Solar Systems
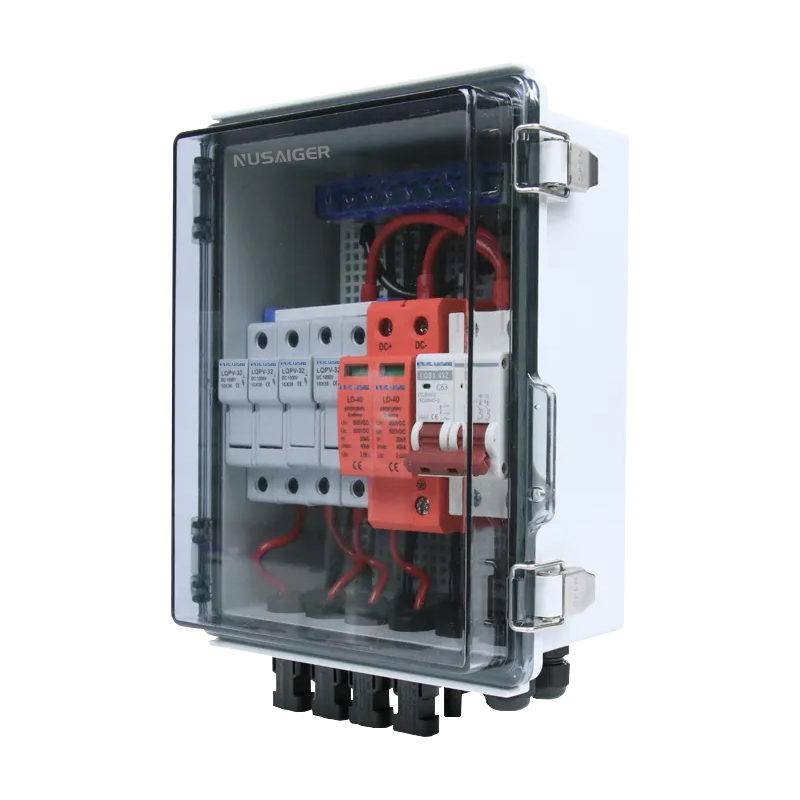
A PV combiner box consolidates outputs from multiple strings of solar panels into a single DC output. Each string typically generates electricity at a specific voltage and current, and without consolidation, managing multiple strings separately would become inefficient. The combiner box simplifies wiring, reduces power loss, and integrates critical safety features like fuses, surge protection devices (SPDs), and disconnect switches.
In addition, modern combiner boxes often come equipped with monitoring systems that allow real-time performance tracking, helping operators quickly identify underperforming strings and optimize energy yield.
3. Key Factors to Consider When Choosing a PV Combiner Box
3.1. System Size and Application
The first step in choosing a PV combiner box is to consider the size and type of your solar installation:
- Residential systems: Usually require smaller combiner boxes supporting fewer strings (2–6 strings).
- Commercial systems: May require mid-sized combiner boxes that handle 6–12 strings with surge protection and monitoring features.
- Utility-scale systems: Large-scale projects often require advanced smart combiner boxes that can manage 12–24 strings, include robust SPDs, and integrate with SCADA systems for remote monitoring.
3.2. Voltage and Current Ratings
Ensure that the combiner box is rated for the maximum DC voltage of your system. Common ratings include 600 VDC, 1000 VDC, and 1500 VDC. The current rating must also be sufficient to handle the combined current of all strings connected to the box.
3.3. Protection Features
High-quality combiner boxes include protective devices that safeguard both the system and personnel:
- Fuses or circuit breakers for overcurrent protection.
- Surge protection devices (SPDs) for lightning or grid-induced surges.
- DC disconnect switch for safe isolation during maintenance.
3.4. Environmental Conditions
Outdoor installations require combiner boxes with high ingress protection (IP65 or higher) to withstand dust, moisture, and UV radiation. For harsh environments such as coastal regions, stainless steel enclosures may be necessary to prevent corrosion.
3.5. Standards and Certifications
Always select a combiner box that complies with relevant international and national standards such as IEC 61439, UL 1741, or NEC Article 690. Certification ensures reliability, safety, and compatibility with other system components.
4. Smart vs. Standard Combiner Boxes
With advancements in solar technology, the market now offers both standard and smart PV combiner boxes. Understanding their differences can help you make an informed decision:
- Standard Combiner Boxes: Provide basic string consolidation, fuses, and disconnect switches. They are cost-effective and suitable for small systems.
- Smart Combiner Boxes: Include additional features like string-level monitoring, communication interfaces (Modbus, RS485, Ethernet), and temperature sensors. These boxes are ideal for medium to large-scale projects where performance monitoring is essential.
5. Installation Considerations
A well-chosen combiner box can still fail if installed incorrectly. Key installation considerations include:
- Mount the combiner box at a location that minimizes cable length and voltage drop.
- Ensure proper grounding and bonding for safety.
- Seal all cable entry points to maintain IP protection rating.
- Label all strings and connections for easy identification and troubleshooting.
- Test insulation resistance and polarity before energizing the system.
6. Cost vs. Performance Balance
While it may be tempting to select the cheapest option, investing in a higher-quality combiner box often pays off in long-term reliability and reduced maintenance costs. Consider total cost of ownership, including downtime risks, replacement parts, and monitoring benefits, rather than focusing solely on initial purchase price.
7. Common Mistakes to Avoid
When selecting a PV combiner box, avoid these frequent errors:
- Choosing a box with insufficient current rating.
- Overlooking surge protection devices in high-risk areas.
- Ignoring environmental factors such as humidity and UV exposure.
- Failing to plan for future system expansion.
8. Case Studies
To illustrate the importance of selecting the right combiner box, consider the following scenarios:
Case Study 1: Residential Rooftop in California
A homeowner installed a 6 kW rooftop PV system with a basic 4-string combiner box. By choosing a weatherproof IP65-rated enclosure with surge protection, the system has operated for five years without significant downtime despite frequent thunderstorms.
Case Study 2: Utility-Scale Solar Farm in India
A 50 MW solar farm required dozens of smart combiner boxes with 1500 VDC ratings. The ability to monitor each string remotely has reduced operation and maintenance (O&M) costs significantly, preventing costly downtime.
9. Maintenance Considerations
Choosing the right combiner box also means planning for long-term maintenance. Look for models with:
- Easy-to-replace fuses and SPDs.
- Accessible design for inspections and testing.
- Built-in monitoring to reduce manual checks.
10. Conclusion
Selecting the right PV combiner box is not just about meeting electrical requirements—it is about ensuring the safety, reliability, and efficiency of the entire solar system. By carefully evaluating system size, voltage and current ratings, protective features, environmental conditions, and certifications, you can make a well-informed decision that minimizes risks and maximizes long-term performance.
Whether you are building a residential rooftop installation or managing a large-scale solar farm, the right combiner box will serve as the backbone of your DC distribution system, protecting your investment and ensuring consistent energy yield.