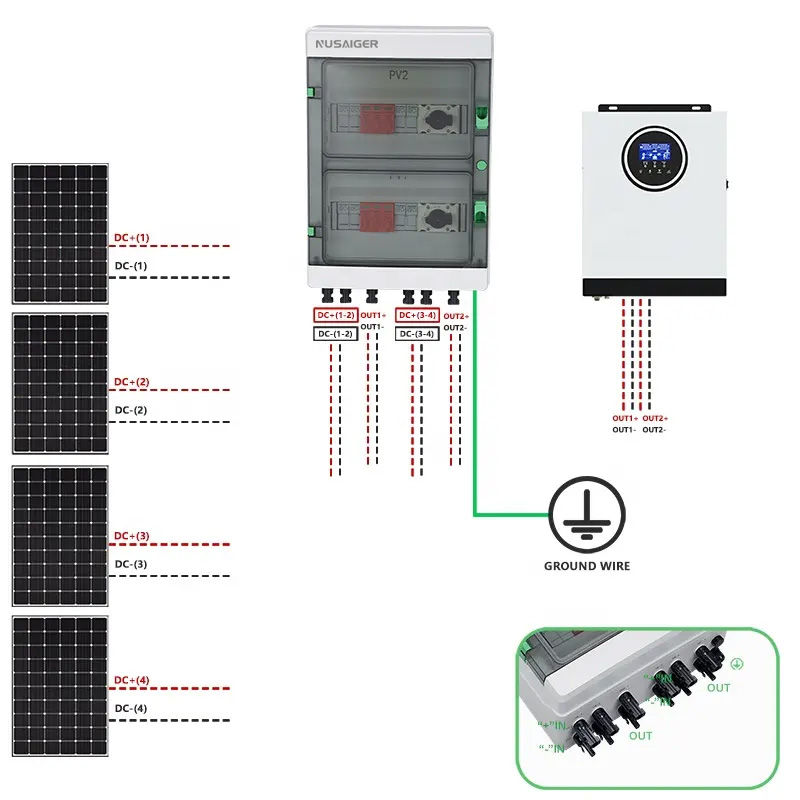
How to Choose the Right PV Combiner Box for Your Project
A complete guide for solar developers, EPCs, and installers to select the most suitable PV combiner box.
1. Introduction
The PV combiner box is a crucial component in any solar project, responsible for consolidating
multiple DC strings into a single output, while providing electrical protection and monitoring.
With multiple options available in the market, choosing the right combiner box requires
careful evaluation of project-specific needs.
This article outlines the key parameters to consider when selecting a PV combiner box
and provides a practical checklist for decision-making.
2. Key Parameters in PV Combiner Box Selection
- Voltage rating: Must match the system design (600V, 1000V, or 1500V DC).
- Current capacity: Adequate for expected string currents and total output.
- Number of inputs (strings): Should fit current array layout and allow expansion.
- Type of protection devices: Fuse, circuit breaker, SPD (surge protection).
- Enclosure type and IP rating: Determines resistance to dust, water, and corrosion.
- Monitoring capabilities: Smart combiner boxes offer data for O&M optimization.
- Certifications: UL, IEC, CE, TÜV, or GB standards depending on region.
3. Voltage and Current Considerations
PV systems are designed for different voltage levels: 600V (older systems), 1000V (commercial),
and 1500V (utility-scale).
The combiner box must be rated for the highest DC voltage expected.
- Check maximum DC input per string.
- Ensure busbars and fuses are sized for combined current.
- Allow 20–25% safety margin for current rating.
4. Number of Strings and Future Expansion
The number of string inputs should match the array layout.
For example, rooftop systems may need 4–8 string inputs, while utility plants may require 16–24 or more.
- Choose modular combiner boxes if future expansion is expected.
- Ensure labeling and monitoring channels align with string count.
5. Protection Devices
Proper protection ensures safety and reliability.
Key devices include:
- Fuses: Protect against overcurrent in each string.
- Circuit breakers: Allow safe manual disconnection.
- SPD (Surge Protection Devices): Safeguard against lightning and transient surges.
Advanced combiner boxes integrate both fuses and SPDs, with replaceable modules for easy maintenance.
6. Enclosure and Environmental Protection
The enclosure must protect internal components from dust, water, and environmental stress.
- IP65/IP66: For outdoor installations.
- NEMA 4X: For harsh environments in North America.
- Corrosion-resistant materials: Stainless steel or UV-resistant plastics for coastal areas.
7. Smart vs. Standard Combiner Boxes
Smart combiner boxes include monitoring functions such as:
- String-level current and voltage measurement.
- Temperature and SPD status monitoring.
- RS485 or Ethernet communication with SCADA systems.
While more expensive, smart combiner boxes reduce O&M costs and improve fault detection.
8. Certification and Compliance
Compliance with standards ensures safety and acceptance by regulators:
- IEC 61439 / IEC 61643: International standards.
- UL 1741: For North American markets.
- CE Marking: Mandatory in Europe.
- TÜV Certification: Globally recognized quality assurance.
- GB Standards: Required in China.
9. Cost vs. Value
Lowest cost is not always the best option. Consider total lifecycle cost:
- Higher upfront cost for smart monitoring can reduce downtime losses.
- Durable enclosures extend service life and reduce replacement costs.
- Certified equipment ensures insurance and warranty validity.
10. Checklist for Selection
- Confirm system voltage and current requirements.
- Select the correct number of string inputs.
- Verify protection devices (fuses, breakers, SPDs).
- Check enclosure IP/NEMA rating for environment.
- Decide between smart and standard models.
- Ensure compliance with local certification standards.
- Evaluate long-term cost vs. performance value.
11. Case Studies
Utility-Scale Solar Farm in India
Selected 1500V combiner boxes with 24 inputs and smart monitoring.
Result: Improved fault detection and reduced O&M cost by 30%.
Commercial Rooftop in Germany
Used 1000V CE-certified boxes with IP66 enclosures.
Result: Long-term durability in wet climate, no corrosion issues after 5 years.
Residential Solar in USA
Installed UL1741 combiner with integrated SPD.
Result: Passed local inspection smoothly and ensured fire safety compliance.
12. Conclusion
Choosing the right PV combiner box requires balancing technical requirements, environmental conditions,
safety certifications, and long-term operational considerations.
A well-selected combiner box not only ensures system reliability but also optimizes investment returns
by reducing downtime and maintenance costs.
Always work with certified manufacturers and align equipment selection with local standards and project goals.