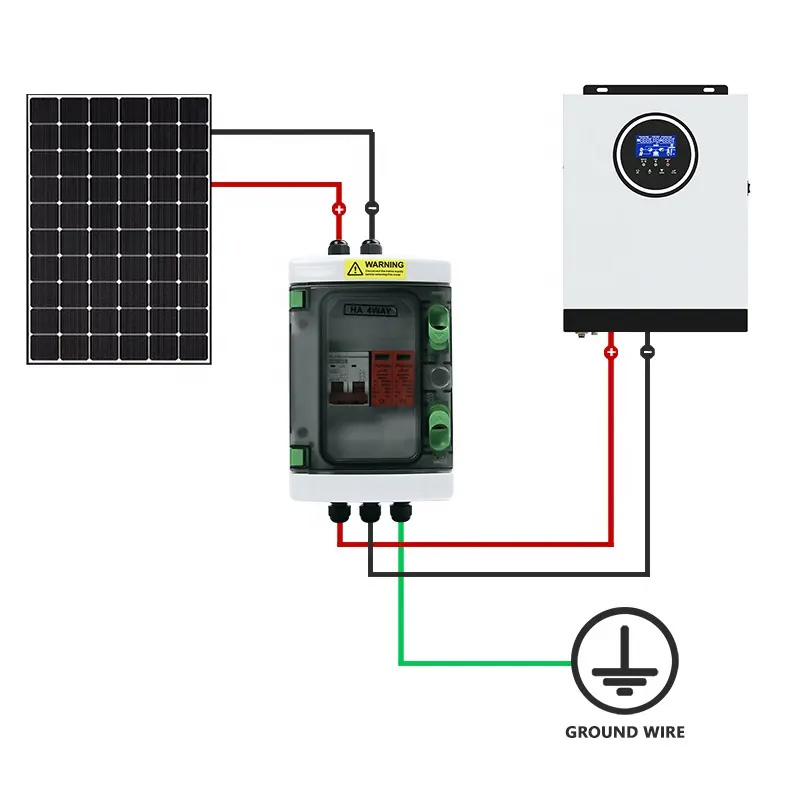
Safety Standards and Certifications for PV Combiner Boxes
A comprehensive guide to global safety compliance for PV combiner boxes in solar projects.
1. Introduction
PV combiner boxes are vital components in solar power systems, consolidating multiple strings and
providing protective functions such as fuses, surge protection devices (SPDs), and circuit breakers.
Given their role in handling high voltages and currents, compliance with safety standards is critical
to prevent electrical hazards, ensure reliability, and meet regulatory requirements.
This article provides an overview of the major international standards and certifications
governing PV combiner boxes, their importance, and how to ensure compliance across regions.
2. Why Safety Standards Matter
- Prevent Hazards: Reduce risks of fire, electric shock, and equipment damage.
- Ensure Reliability: Certified components are tested for long-term performance.
- Regulatory Compliance: Certification is often legally required for installations.
- Customer Trust: Certified products assure investors and end-users of quality.
- International Trade: Standards allow global acceptance and reduce market barriers.
3. International Standards Overview
PV combiner boxes must comply with various international standards depending on region and application.
Below are the key standards that manufacturers and installers must understand.
- IEC Standards (International): Commonly adopted across Europe, Asia, and Africa.
- UL Standards (North America): Mandatory for the U.S. and Canadian markets.
- CE Marking (Europe): Compliance with EU directives for product safety.
- TÜV Certification (Global): Independent testing for reliability and quality assurance.
- GB Standards (China): National standards for PV equipment within China.
4. IEC Standards for PV Combiner Boxes
IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission) sets global benchmarks for PV safety and performance.
- IEC 61439: General requirements for low-voltage switchgear and controlgear assemblies.
- IEC 62109: Safety requirements for power converters and associated equipment.
- IEC 61643: Standards for surge protective devices.
- IEC 60529: Ingress protection (IP rating) requirements for enclosures.
5. UL Standards (North America)
In the United States and Canada, UL standards are mandatory for electrical equipment certification.
- UL 1741: Inverters, converters, controllers, and PV combiner boxes.
- UL 508A: Industrial control panels, including combiner box assemblies.
- UL 1449: Safety requirements for surge protective devices.
6. CE Marking (Europe)
CE certification indicates compliance with EU health, safety, and environmental requirements.
- Low Voltage Directive (LVD) 2014/35/EU – Covers equipment operating at 50–1000 V AC or 75–1500 V DC.
- EMC Directive 2014/30/EU – Electromagnetic compatibility standards.
- RoHS Directive 2011/65/EU – Restriction of hazardous substances in materials.
7. TÜV Certification
TÜV Rheinland and TÜV SÜD provide independent testing and certification for PV equipment.
TÜV certification is highly recognized worldwide and often complements IEC and CE compliance.
- Verifies mechanical and electrical durability.
- Assures safety in harsh environments (temperature, humidity, UV exposure).
- Confirms SPD and fuse performance under surge conditions.
8. Chinese GB Standards
In China, PV combiner boxes must comply with GB (Guobiao) standards:
- GB/T 7251: Low-voltage switchgear assemblies.
- GB/T 3859: Safety for power electronic equipment.
- GB/T 36234: Technical requirements for PV DC combiner boxes.
9. Key Certification Tests
During certification, combiner boxes undergo rigorous testing to ensure compliance:
- Dielectric withstand test (insulation strength).
- Thermal cycling and humidity resistance tests.
- Short-circuit withstand capability.
- Ingress protection (IP65/IP66 for outdoor use).
- Salt mist and corrosion resistance for coastal areas.
10. Regional Differences in Standards
Different markets prioritize different compliance marks:
- North America: UL certification is mandatory.
- Europe: CE marking is essential for legal sale.
- Middle East & Africa: IEC/TÜV certifications are widely accepted.
- China: GB standards compliance required.
- Australia: Both IEC and local AS/NZS standards apply.
11. Importance for Installers and Developers
Choosing certified combiner boxes ensures legal compliance and reduces risks.
Installers and project developers must verify certification documents and match them with local regulations.
- Always request certification reports from suppliers.
- Ensure certification matches specific model numbers.
- Cross-check validity on certification bodies’ websites.
12. Future Trends in PV Combiner Box Certification
- Integration of cybersecurity standards for IoT-enabled combiner boxes.
- Stricter fire safety standards for lithium battery hybrid systems.
- Global harmonization of IEC and UL requirements.
- Environmental sustainability certifications (low-carbon materials).
13. Conclusion
Compliance with safety standards and certifications is not optional—it is fundamental for safe,
reliable, and legally approved solar installations.
From IEC and UL to CE, TÜV, and GB standards, each plays a critical role in ensuring PV combiner
boxes meet stringent requirements.
For project developers, choosing certified equipment guarantees both performance and peace of mind,
safeguarding investments for the long term.